MCP Server which shares context between sub-agent for Claude Code
sqlew

Never Start From Zero Context Again – An MCP server that gives AI agents a shared SQL-backed context repository
What is sqlew?
sqlew is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that provides AI agents with a shared SQL-backed context repository across sessions.
Concerns About AI Coding
Every Claude session starts with zero context. You must re-explain decisions, agents can reintroduce bugs, and there's no way to track WHY decisions were made.
It is possible to keep records using Markdown files. However, maintaining records for large-scale projects and long-term maintenance generates an enormous volume of documentation.
This has become problematic because it causes context rotting in AI systems, leading to performance deterioration.
sqlew provides the solution for this problem
sqlew builds an efficient external context repository for AI by using relational databases.
- Records the reasoning behind decisions
- Enables querying past context
- Prevents anti-patterns through constraints
- Eliminates duplicate work via task management
This software does not send any data to external networks. We NEVER collect any data or usage statistics. Please use it with complete security.
Concept: Decision & Constraint Repository Layer
sqlew originally started as a way to reduce duplicated work and inconsistent behavior across multiple AI agents. Instead of letting every new session re-read the same documents and reinvent similar code, sqlew centralizes context in a shared SQL database.
With recent LLMs, the most valuable part of this shared context has proved to be the history of Decisions and Constraints:
- Decisions capture why a change or design choice was made (trade-offs, rejected options, rationale).
- Constraints capture how things should be done (coding rules, architecture boundaries, performance requirements).
Modern versions of sqlew treat this decision & constraint history as first-class data:
- The database schema is optimized around Decisions and Constraints instead of generic notes.
- A three-tier duplicate detection and suggestion system helps you reuse existing Decisions/Constraints instead of creating nearly identical ones.
- Legacy, unused features have been removed or simplified to keep the focus on long-term context and consistency.
In practice, sqlew acts as a Decision & Constraint repository layer for your AI tools: agents can query what was decided before, which rules already exist, and how similar situations were handled previously.
Why Use sqlew?
🧠 Organizational Memory
Traditional code analysis like git tells you WHAT is done, sqlew adds WHY and HOW on it:
- Decisions → WHY it was changed
- Constraints → HOW should it be written
- Tasks → WHAT needs to be done
⚡ Token Efficiency
60-75% token reduction in multi-session projects through structured data storage and selective querying.
🎯 Key Benefits for Your Development Workflow
🧠 Context Persistence Across Sessions
- No More Re-Explaining: AI remembers decisions from weeks ago - no need to re-explain "why we chose PostgreSQL over MongoDB"
- Session Continuity: Pick up exactly where you left off, even after days or weeks
- Team Knowledge Sharing: New team members (or new AI sessions) instantly understand past decisions
🛡️ Prevents Context Rotting & Inconsistency
- Architectural Constraints: Define rules once ("always use async/await, never callbacks"), AI follows them forever
- Version History: Track how decisions evolved - see what changed and when
🎯 Enables Consistent, High-Quality Code
- Bug Prevention: AI won't reintroduce bugs you already fixed (decisions document "what didn't work")
- Pattern Enforcement: Constraints ensure AI writes code matching your team's style
- Context-Aware Suggestions: AI sees related decisions before creating new ones ("Did you know we already solved this?")
- Rationale Documentation: Every decision includes WHY it was made, preventing cargo-cult programming
📊 Transparent AI Work Tracking
- Task Dependencies: AI knows Task B needs Task A completed first
- Auto File Watching: Tasks auto-update when AI edits tracked files (zero manual updates)
- Progress Visibility: See exactly what AI is working on, what's blocked, what's done
⚡ Efficiency & Reliability
- 60-75% Token Reduction: Structured data beats dumping entire context into prompts
- Reduce Context Rot: No more "this README is 50 pages and AI ignores half of it"
- Production-Ready: 495/495 tests passing (100%), battle-tested on real projects
Technical Features: 6 specialized MCP tools (decisions, tasks, files, constraints, stats, suggest), smart similarity scoring (0-100 point algorithm), runtime reconnection, parameter validation, metadata-driven organization
See docs/TASK_OVERVIEW.md and docs/DECISION_CONTEXT.md for details.
🔖Kanban-style AI Scrum
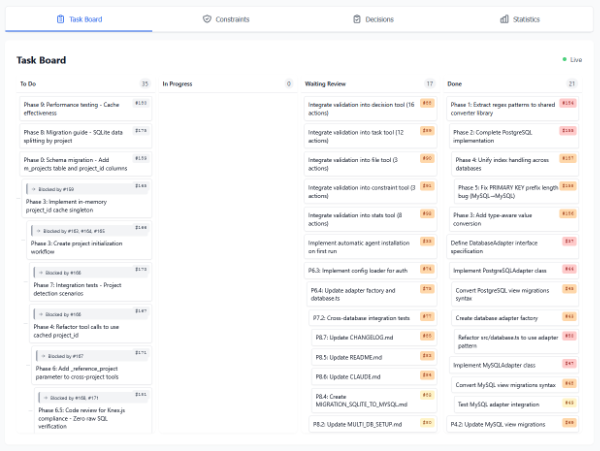
(This visualizer is not included in this package)
Installation
Requirements
- Node.js 20.0.0 or higher
- npm or npx
Quick Install
on .mcp.json in your project's root, add these lines:
{
"mcpServers": {
"sqlew": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["sqlew"]
}
}
}
Recommend to restart claude after initialize
The first time, sqlew initializes database, installs custom agents and slash commands. But agents and commands are not loaded in this time. So, please exit claude once, and restart claude again.
It's Ready!
🚀 Quick Start: /sqlew Command
The /sqlew command is the easiest way to use sqlew! Just type /sqlew in Claude Code with natural language input.
Most Common Uses
# Show status and get suggestions
/sqlew
# Record a decision
/sqlew record we use PostgreSQL 15 for production database
# Search past decisions
/sqlew search why we chose Knex for migrations
# List remaining tasks
/sqlew show remaining tasks
# Plan a new feature (breakdown into tasks)
/sqlew plan implementing user authentication
The /sqlew command automatically detects your intent (search, record, list, execute, task creation) and invokes the appropriate MCP tools.
⚠️Note: Global install (npm install -g) is not recommended because sqlew requires an independent settings per project. Each project should maintain its own context database in .sqlew/sqlew.db.
Custom database path: Add path as argument: "args": ["sqlew", "/path/to/db.db"]
Default location: .sqlew/sqlew.db
⚠️ Not Supported: Junie AI cannot use relative paths in MCP server configurations, which makes it incompatible with sqlew's project-based database model. Each project requires its own isolated database at .sqlew/sqlew.db, but Junie AI's global MCP configuration cannot handle per-project database paths.
Configuration
Database Support
sqlew supports multiple database backends for different deployment scenarios:
| Database | Use Case | Status | |----------|----------------------------------------------|-------------| | SQLite | Personal or small projects | ✅ Default | | MySQL 8.0 / MariaDB 10+ | Production, shared environments, remote work | ✅ Supported | | PostgreSQL 12+ | Production, shared environments, remote work | ✅ Supported |
Of course, it also works with Docker RDB instances.
Optional Config File
On first run, .sqlew/config.toml will be created for persistent settings:
SQLite (Default):
[database]
path = ".sqlew/custom.db"
[autodelete]
ignore_weekend = true
message_hours = 48
PostgreSQL:
[database]
type = "postgres"
[database.connection]
host = "localhost"
port = 5432
database = "sqlew_db"
[database.auth]
type = "direct"
user = "sqlew_user"
password = "secret"
MySQL/MariaDB:
[database]
type = "mysql"
[database.connection]
host = "localhost"
port = 3306
database = "sqlew_db"
[database.auth]
type = "direct"
user = "sqlew_user"
password = "secret"
Also .sqlew/config.example.toml is created for reference.
Settings Priority: CLI args > config.toml > database defaults
See docs/CONFIGURATION.md for all options and validation rules.
CLI Configuration (Recommended)
Configuration is managed via .sqlew/config.toml file and CLI arguments only. The MCP config tool has been removed for simplicity.
Why CLI-only configuration?
- No drift: Single source of truth (config file)
- Version control: Commit config to git, share with team
- Clear documentation: Config file documents project requirements
- Type safety: TOML validation catches errors at startup
Common CLI arguments:
# Custom database path
npx sqlew /path/to/database.db
# Auto-deletion settings
npx sqlew --autodelete-message-hours=48
npx sqlew --autodelete-file-history-days=30
npx sqlew --autodelete-ignore-weekend
# Custom config file
npx sqlew --config-path=.sqlew/custom.toml
For persistent settings, edit .sqlew/config.toml instead of using CLI arguments.
Quick Start
install it, launch claude, exit claude and launch Claude again.
Basic Usage
You'll never need to call it manually, I recommend to call this tool via prompt.
read sqlew usecases, and plan implementation of feature X using sqlew.
or invoke Specialized Agent
/sqw-plan implementation of feature X .
Specialized Agents use sqlew more efficiently.
Note: The /sqlew command supersedes the previous multi-command system (/sqw-plan, /sqw-scrum, etc.). All functionality is now available through the unified /sqlew interface with automatic intent detection.
Advanced: Direct MCP Tool Access
Power users can still call MCP tools directly. See Available Tools section below.
Available Tools
| Tool | Purpose | Example Use | |------|---------|------------| | decision | Record choices and reasons | "We chose PostgreSQL" | | constraint | Define rules | "DO NOT use raw SQL, use ORM" | | task | Track work | "Implement feature X" | | file | Track changes | "Modified auth.ts" | | stats | Database metrics | Get layer summary | | suggest | Find similar decisions (v3.9.0) | Duplicate detection, pattern search |
Documentation
Each tool supports action: "help" for full documentation and action: "example" for comprehensive usage examples.
And action: "use_case" shows how to use the tool in a real-world scenario.
On-Demand Documentation
All tools support:
action: "help"- Parameter reference and descriptionsaction: "example"- Usage scenarios and examplesaction: "use_case"- Real-world usage examples
For AI Agents
Essential Guides:
- Tool Selection - Decision tree, when to use each tool
- Workflows - Multi-step examples, multi-agent coordination
- Tool Reference - Parameters, batch operations, templates
- Best Practices - Common errors, troubleshooting
Task System:
- Task Overview - Lifecycle, status transitions
- Task Actions - All actions with examples
- Task Dependencies - Blocking relationships
- Task Linking - Link to decisions/constraints/files
- Task Migration - Migrate from decision-based tracking
Advanced Features:
- Decision Intelligence - Three-tier duplicate detection (v3.9.0)
- Decision Context - Rich decision documentation
- Auto File Tracking - Zero-token task management
- Acceptance Criteria - All check types
Reference:
- Shared Concepts - Layer definitions, enum values
- Configuration - Config file setup, all options
- Architecture - Technical architecture
Advanced Usage
- Configuration Guide - TOML config file setup
- CLI Mode Overview - Database migration, export/import commands
- Building from Source - Setup instructions
- Migration Guides - Version upgrade guides
Use Cases
- Multi-Agent Coordination: Orchestrators create tasks, agents send status updates
- Breaking Change Management: Record deprecations and add architectural constraints
- Decision Context: Document rationale, alternatives considered, and trade-offs
- Session Continuity: Save progress in Session 1, resume in Session 2
See docs/WORKFLOWS.md for detailed multi-step examples.
Performance
- Query speed: 2-50ms
- Concurrent agents: 5+ simultaneous
- Storage efficiency: ~140 bytes per decision
- Token savings: 60-75% in typical projects
Support
Support development via GitHub Sponsors - One-time or monthly options available.
Version
Current version: 4.0.2 See CHANGELOG.md for release history.
What's New in v4.0.2:
- Unified CLI Entry Point -
npx sqlew db:exportworks directly (nonpm installrequired) - Cross-DB Migration via JSON Only - SQL dump no longer supports cross-database conversion
- Node.js 20+ Required - Updated minimum version requirement
What's New in v4.0.0:
- Schema Refactoring - Unified v4_ table prefix, agent system completely removed
- Clean Schema - No legacy columns, optimized for Decision & Constraint repository
- Improved Migration System - Reorganized v3/v4 directories
See docs/DECISION_INTELLIGENCE.md for details on the suggest tool.
License
AGPLv3 - Free to use. Open-source required when embedding or modifying. See LICENSE for details.
Links
Support & Documentation
- Issues: GitHub Issues
- Docs: docs/ directory
Acknowledgments
Built with Model Context Protocol SDK, better-sqlite3, and TypeScript.
Author: sin5ddd

