Saleforce MCP Neo4j Demo
🚀 Integrating Salesforce with Neo4j Using MCP, RAG & LWC – A Practical Demo of Three Architectures
In this demo, I showcase three different architectures where Salesforce interacts with Neo4j graph database using Modern Context Protocol (MCP), GraphRAG, and custom Node.js gateway logic.
My goal was simple:
👉 Expose Neo4j as a knowledge graph backend to Salesforce in a way that developers can query graph data using natural language, Cypher, or intelligent RAG translation.
🎯 The Three Integration Methods
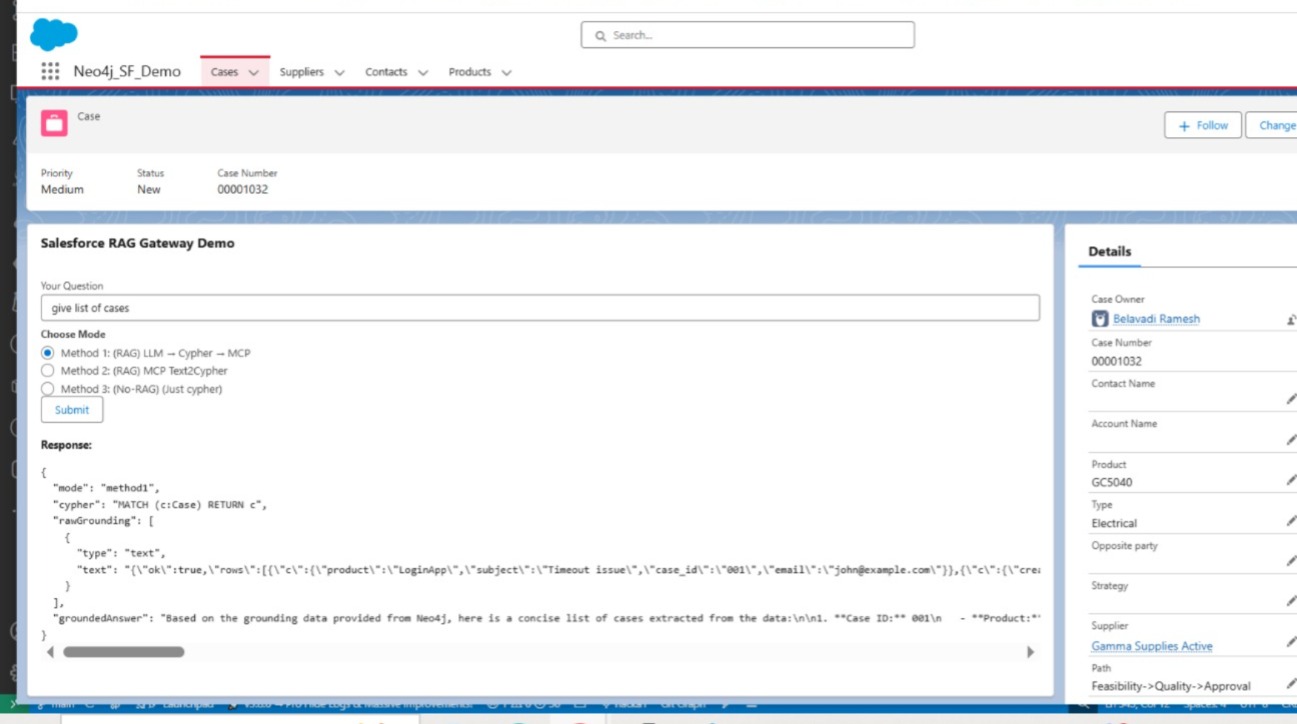
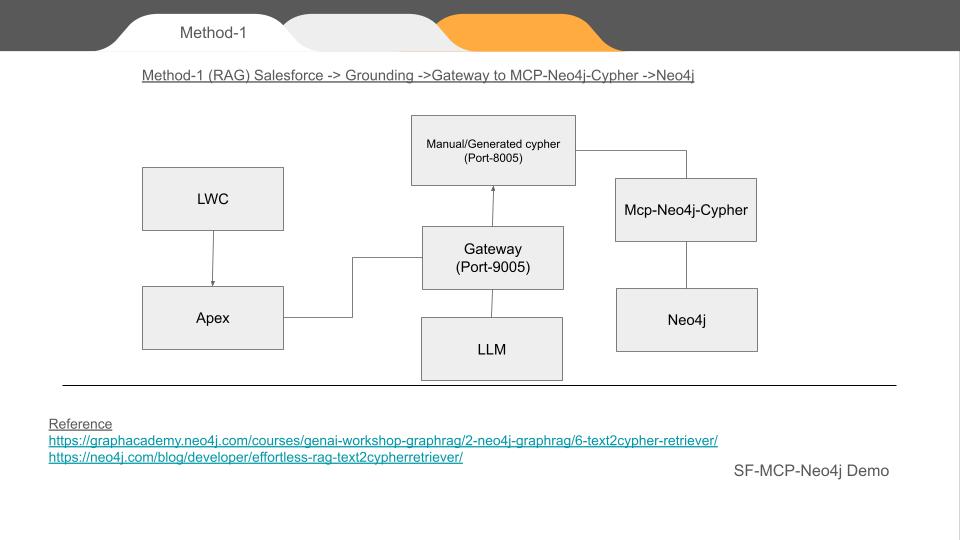
✅ Method 1 – RAG with Direct MCP-Neo4j-Cypher
Salesforce → Grounding → Node.js Gateway → MCP-Neo4j-Cypher → Neo4j
In this method, Salesforce sends a natural language request. The MCP tool translates it to Cypher using grounding logic and executes it directly against Neo4j.
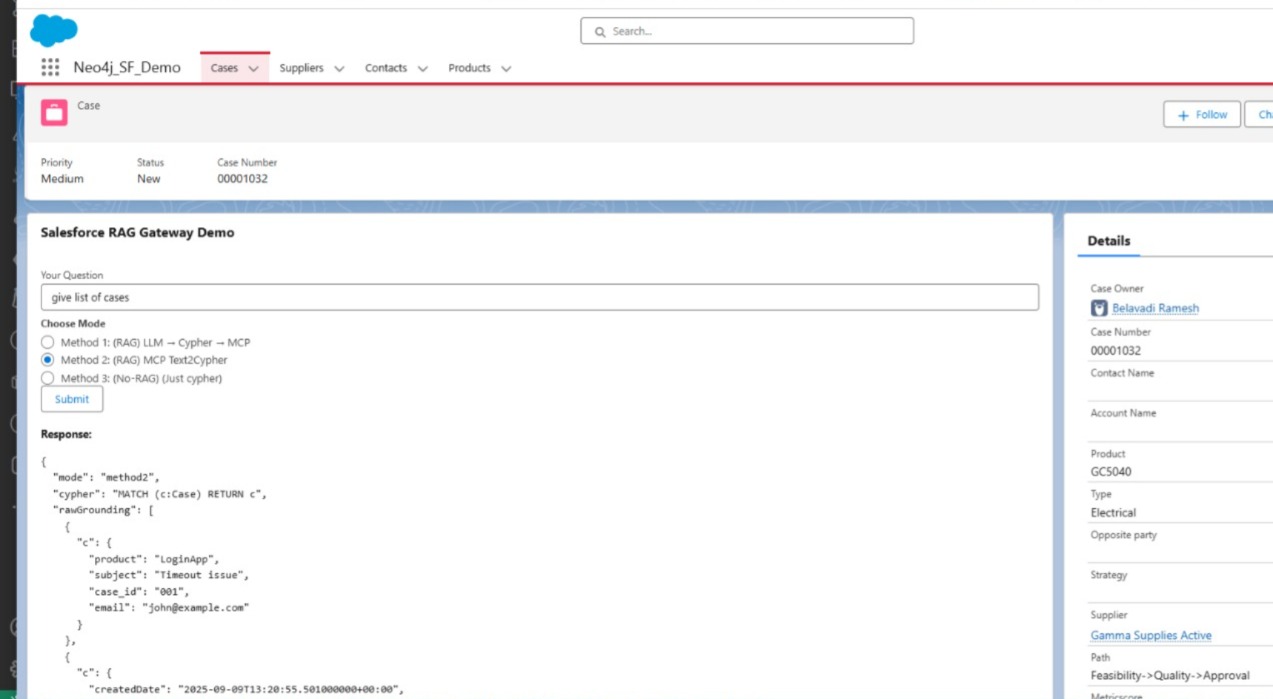
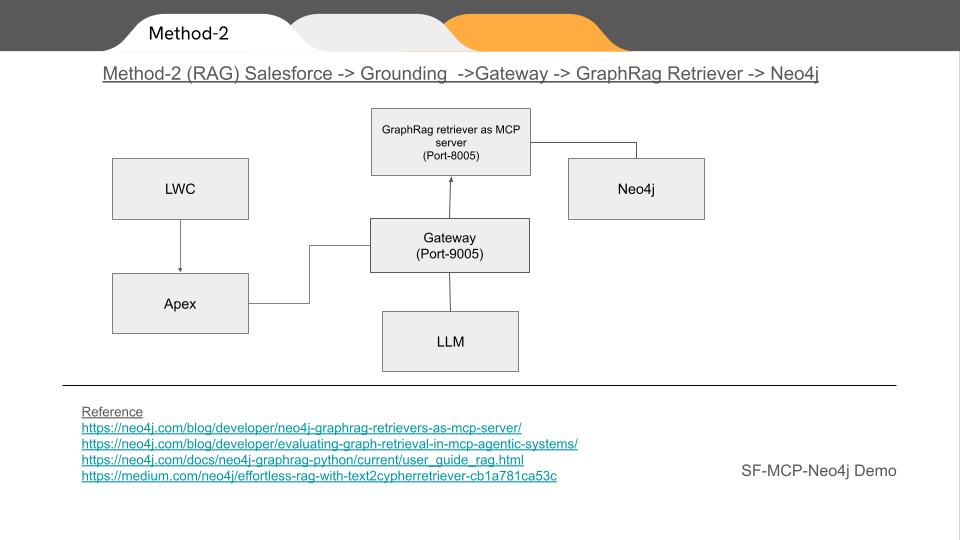
✅ Method 2 – RAG with GraphRag Retriever
Salesforce → Grounding → Node.js Gateway → GraphRAG Retriever → Neo4j
Here, instead of translating NL to Cypher directly, we use GraphRAG Text2CypherRetriever. It returns context-aware Cypher suggestions with top_k ranking before execution.
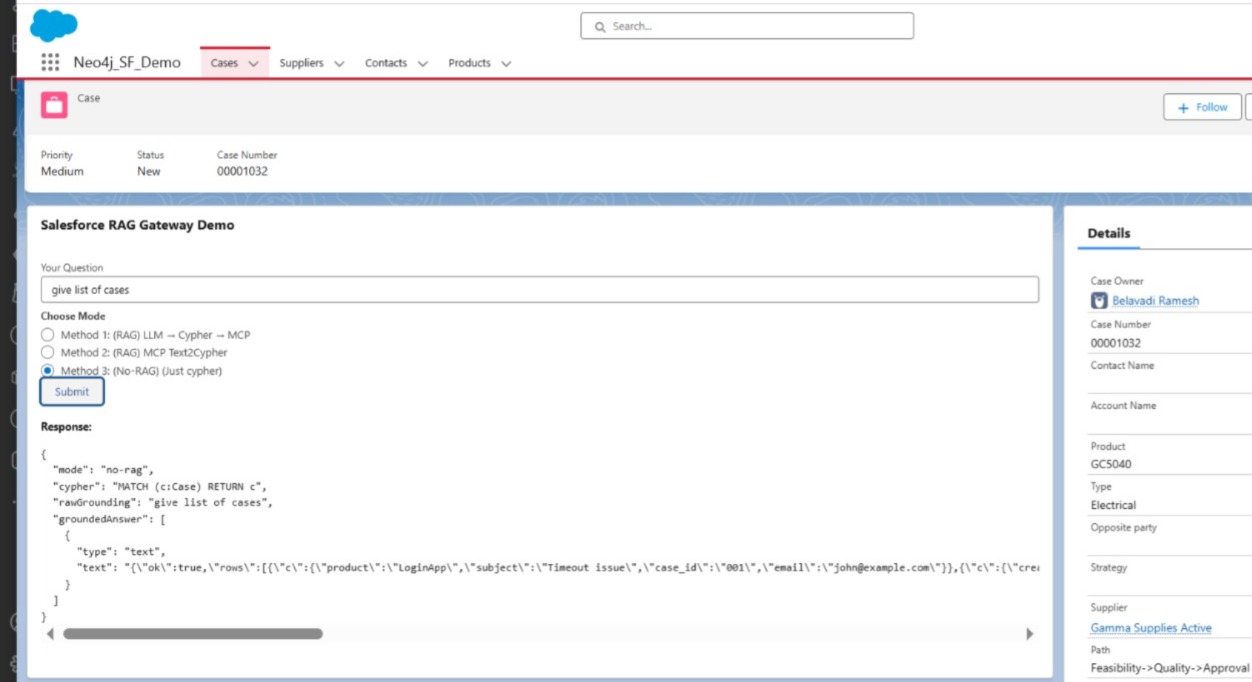
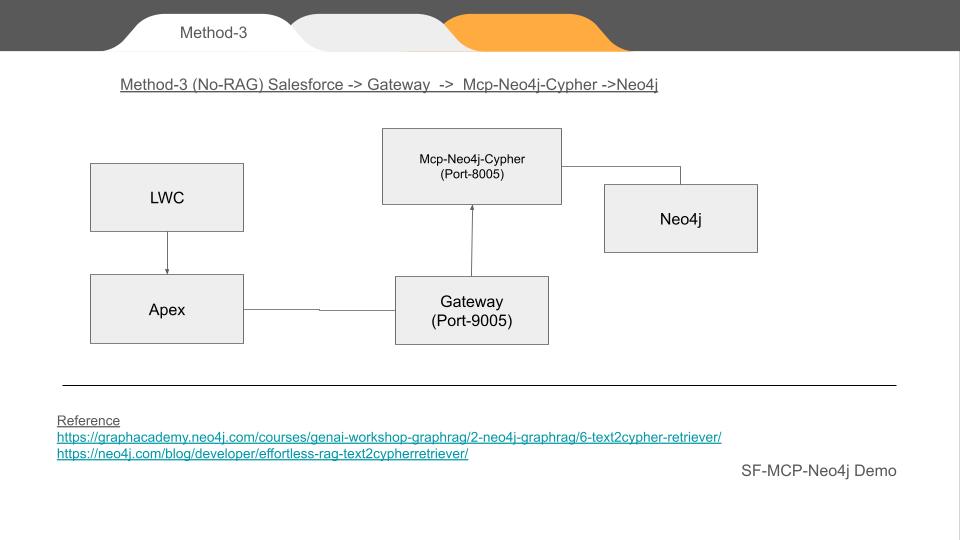
✅ Method 3 – Direct Cypher Execution (No-RAG Mode)
Salesforce → Node.js Gateway → MCP-Neo4j-Cypher → Neo4j
This is the developer mode. We bypass grounding and RAG. Salesforce submits a Cypher query directly, routed via MCP.
🏗 Architecture Overview
| Layer | Component |
|-------|----------|
| UI Layer | Lightning Web Component (LWC) |
| Backend (Salesforce) | Apex Controller → Named Credentials → HTTP Callouts |
| Gateway | Node.js MCP Client Gateway (Port 9005) |
| MCP Services | Python MCP Server (Port 8005) exposing text2cypher and read-cypher |
| Data Layer | Neo4j Graph Database |
- LWC sends requests → Apex
- Apex uses Named Credentials + ngrok HTTPS endpoint
- Node.js Gateway converts Salesforce HTTP into MCP requests
- Python MCP Server hosts tools that translate or execute Cypher
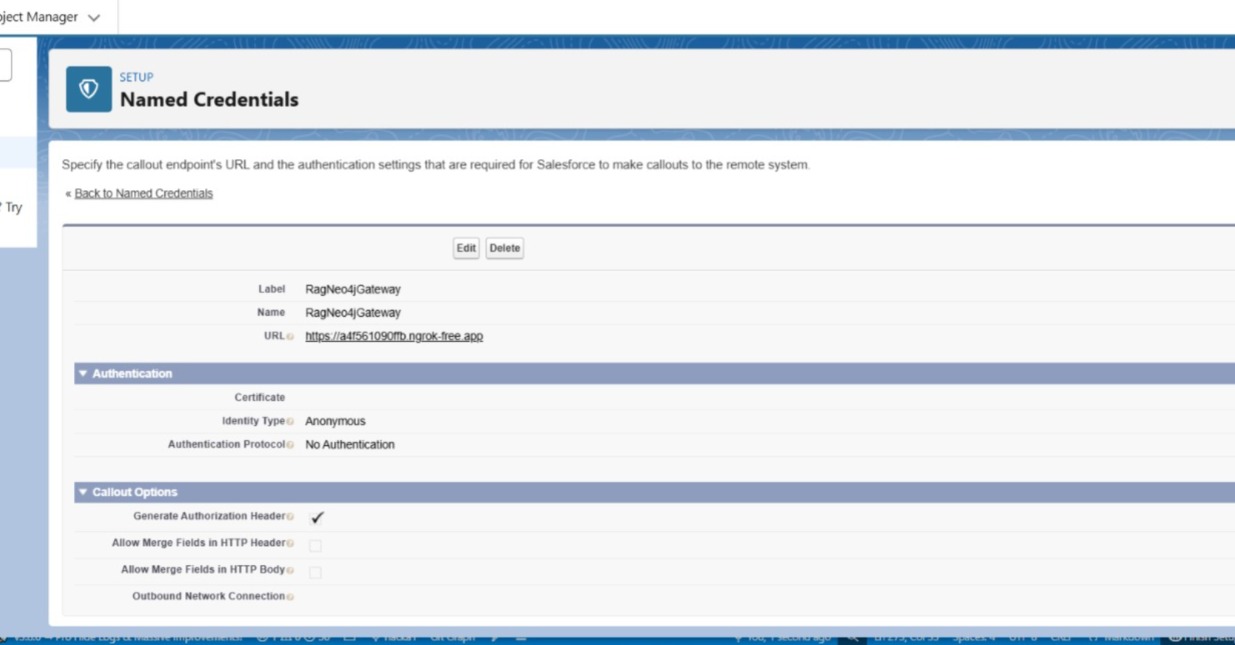
🎛 Why Apex + Named Credentials?
Salesforce does not allow direct HTTP calls from LWC due to security policy. So:
- Apex makes the callout
- Named Credential exposes the gateway URL
- Ngrok provides temporary HTTPS URL, because Named Credentials do not accept HTTP
🛠 MCP Tools Implemented (Python)
# -----------------------
# Tool: text2cypher (GraphRAG)
# -----------------------
@mcp.tool(name="text2cypher")
def text2cypher_tool(query: str, top_k: int = 3):
"""
Use Neo4j GraphRAG Text2CypherRetriever to generate Cypher via rag.search().
"""
try:
# ✅ Call correct official API for latest neo4j-graphrag
result = rag.search(query_text=query)
# The retriever can also be used without using graphRag
# result = retriever.search(query_text=query)
print (result)
# fallback if result.cypher_query is missing
cypher_query = (
getattr(result, "cypher_query", None)
or getattr(result, "cypher", None)
or getattr(result, "query", None)
or (getattr(result, "metadata", {}) or {}).get("cypher")
or (getattr(result, "metadata", {}) or {}).get("cypher_text")
)
# ✅ Extract fields safely
graph_data = getattr(result, "records", None)
if not cypher_query:
return {"error": "No Cypher generated", "raw": str(result)}
# ✅ Execute Cypher via standard Neo4j session
with driver.session() as session:
data_rows = session.run(cypher_query)
final_data = [record.data() for record in data_rows]
return {
"input": query,
"cypher": cypher_query,
"graphData": final_data
}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": str(e)}
# -----------------------
# Helpers
# -----------------------
def _execute_cypher_return_rows(cypher_text: str, params: dict | None = None):
"""Execute a cypher string in read mode and return list of record.data() dicts."""
params = params or {}
with driver.session(default_access_mode="READ") as session:
result = session.run(cypher_text, **params)
return [rec.data() for rec in result]
# -----------------------
# Tool: read_neo4j_cypher
# -----------------------
@mcp.tool(name="read_neo4j_cypher")
def read_neo4j_cypher(query: str):
"""
Execute read-only Cypher and return rows.
"""
try:
rows = _execute_cypher_return_rows(query)
return {"ok": True, "rows": rows}
except Exception as e:
return {"ok": False, "error": str(e), "trace": traceback.format_exc()}
🛠 Gateway Implemented (Node.js)
// 1) Method 1: LWC -> Gateway -> translateToCypher(LM) -> MCP read_neo4j_cypher -> groundedAnswer -> return
app.post('/method1', async (req, res) => {
try {
const { naturalLanguage } = req.body;
const cypherQuery = await translateToCypher(naturalLanguage);
const client = await mcpClientPromise;
const result = await client.callTool({ name: 'read_neo4j_cypher', arguments: { query: cypherQuery } });
console.log(result);
const grounded = await groundedAnswer(naturalLanguage, result.content?.json || result.content?.text || result, cypherQuery);
res.json({ mode: 'method1', cypher: cypherQuery, rawGrounding: result.content || null, groundedAnswer: grounded });
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
res.status(500).json({ error: err.message });
}
});
// 2) Method 2: LWC -> Gateway -> MCP text2cyphertool -> returns cypher + grounding -> groundedAnswer -> return
app.post('/method2', async (req, res) => {
console.log("method2 LWC -> Gateway -> MCP text2cyphertool");
try {
const { naturalLanguage } = req.body;
const client = await mcpClientPromise;
// Call the MCP tool that exposes text2cypher retriever on the Neo4j side
const toolResult = await client.callTool({ name: 'text2cypher', arguments: { query: naturalLanguage } });
console.log(toolResult);
// Expect toolResult.content to include { cypherQuery, graphData }
// const cypherQuery = toolResult.content?.json?.cypherQuery || toolResult.content?.json?.cypher || (toolResult.content?.text || '').slice(0, 2000);
const contentBlock = toolResult.content?.[0];
if (contentBlock?.type === 'text' && contentBlock.text) {
const parsed = JSON.parse(contentBlock.text);
cypherQuery = parsed.cypher || parsed.cypherQuery || parsed.metadata?.cypher;
graphData = parsed.graphData || parsed.rows || parsed.records || parsed.data;
}
console.log("cypherQuery = " + cypherQuery);
// const graphData = toolResult.content?.json?.graphData || toolResult.content?.json?.rows || toolResult.content?.text || toolResult.content || {};
console.log("graphData = " + graphData);
const grounded = await groundedAnswer(naturalLanguage, graphData, cypherQuery);
console.log("grounded = " + grounded);
res.json({ mode: 'method2', cypher: cypherQuery, rawGrounding: graphData, groundedAnswer: grounded });
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
res.status(500).json({ error: err.message });
}
});
// 3) No-RAG: direct query to DB
app.post('/no-rag', async (req, res) => {
try {
const { naturalLanguage } = req.body;
const cypherQuery = await translateToCypher(naturalLanguage);
const client = await mcpClientPromise;
const result = await client.callTool({ name: 'read_neo4j_cypher', arguments: { query: cypherQuery } });
console.log(result);
res.json({ mode: 'no-rag', cypher: cypherQuery, rawGrounding: naturalLanguage, groundedAnswer: result.content || null });
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
res.status(500).json({ error: err.message });
}
});
🌍 Testing via cURL
curl -X POST https://a4f561090ffb.ngrok-free.app/method2 -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d @naturaldemo.json
Input JSON (naturaldemo.json)
{"naturalLanguage": "Find list of cases"}
Response
curl -X POST https://a4f561090ffb.ngrok-free.app/method2 -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d @naturaldemo.json
{"mode":"method2","cypher":"MATCH (c:Case) RETURN c","rawGrounding":[{"c":{"product":"LoginApp","subject":"Timeout issue","case_id":"001","email":"john@example.com"}},{"c":{"createdDate":"2025-09-09T13:20:55.501000000+00:00","subject":"Cannot login","caseNumber":"00012345","id":"5005j00001ABC123","priority":"High","status":"Closed"}},{"c":{"createdDate":"2025-09-09T13:20:55.501000000+00:00","subject":"Payment failed","caseNumber":"00012346","id":"5005j00001ABC456","priority":"Medium","status":"In Progress"}},{"c":{"subject":"The server is crashing in weekend"}}],"groundedAnswer":"To find the list of cases from the provided grounding data, we can extract the relevant information from each case entry. The grounding data contains several cases with different attributes. Here’s a concise summary of the cases identified:\n\n1. **Case ID: 001**\n - **Product:** LoginApp\n - **Subject:** Timeout ....
...
}
💻 Apex Code to access Gateway (RagGatewayController)
public with sharing class RagGatewayController {
@AuraEnabled(cacheable=false)
public static Object getMcpResponse(String input, String mode) {
Http http = new Http();
HttpRequest req = new HttpRequest();
String baseUrl = 'callout:RagNeo4jGateway/'; // Replace with actual host
String endpoint = baseUrl + '/' + mode; // mode = method1, method2, no-rag
req.setEndpoint(endpoint);
req.setMethod('POST');
req.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');
Map<String, Object> payload = new Map<String, Object>{ 'naturalLanguage' => input };
req.setBody(JSON.serialize(payload));
HttpResponse res = http.send(req);
if (res.getStatusCode() == 200) {
return JSON.deserializeUntyped(res.getBody());
} else {
throw new AuraHandledException('Gateway error: ' + res.getStatus());
}
}
}
💻 Apex Test Code (Anonymous Execution)
try {
String input = 'Find suppliers in Bangalore';
String mode = 'method1'; // method2, no-rag also valid
Object result = RagGatewayController.getMcpResponse(input, mode);
System.debug('✅ Result:
' + JSON.serializePretty(result));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.debug('❌ Exception: ' + e.getMessage());
}
🔌 Gateway (Node.js MCP Client) – Runs on 9005
Acts as HTTP to MCP bridge. Receives
/method1,/method2,/no-ragPOST and forwards to MCP server.
🐍 Python MCP Server – Runs on 8005
Exposes GraphRAG Text2CypherRetriever and read-only Cypher execution.
🎨 LWC App – UI Layer
- 3 buttons → Method 1, Method 2, No-RAG
- Input field for natural language
- Displays JSON result from Neo4j via gateway
import { LightningElement, track } from 'lwc';
import getMcpResponse from '@salesforce/apex/RagGatewayController.getMcpResponse';
export default class RagGatewayDemo extends LightningElement {
@track userInput = '';
@track selectedMode = 'method1';
@track response;
modeOptions = [
{ label: 'Method 1: (RAG) LLM → Cypher → MCP', value: 'method1' },
{ label: 'Method 2: (RAG) MCP Text2Cypher', value: 'method2' },
{ label: 'Method 3: (No-RAG) (Just cypher)', value: 'no-rag' }
];
handleInput(event) {
this.userInput = event.target.value;
}
handleModeChange(event) {
this.selectedMode = event.detail.value;
}
async handleSubmit() {
try {
const result = await getMcpResponse({ input: this.userInput, mode: this.selectedMode });
this.response = JSON.stringify(result, null, 2);
} catch (error) {
this.response = 'Error: ' + error.body.message;
}
}
}
LWC html
<template>
<lightning-card title="Salesforce RAG Gateway Demo">
<div class="slds-p-around_medium">
<lightning-input label="Your Question" value={userInput} onchange={handleInput}></lightning-input>
<lightning-radio-group
name="mode"
label="Choose Mode"
options={modeOptions}
value={selectedMode}
onchange={handleModeChange}>
</lightning-radio-group>
<lightning-button label="Submit" onclick={handleSubmit} class="slds-m-top_medium"></lightning-button>
<template if:true={response}>
<p class="slds-m-top_medium"><strong>Response:</strong></p>
<pre>{response}</pre>
</template>
</div>
</lightning-card>
</template>
📸 Screenshots
- 📷 LWC with 3 tabs
🔮 Final Thoughts
This experiment proves that Salesforce is no longer just CRM – it can orchestrate graph intelligence via MCP and Neo4j. With GraphRAG, grounded cypher generation, and structured MCP tools, we can turn Salesforce into a graph-aware intelligent console.